The
PhilPaSSplus is the lone Peso Real-Time Gross Settlement (RTGS) system in the Philippines, owned and operated by the Bangko Sentral ng Pilipinas (BSP) in accordance with its authority under the National Payment Systems Act. An RTGS system provides instant settlement of payments, transfer instructions, or other obligations individually on a transaction-by-transaction basis1.
The
PhilPaSSplus enables the efficient and low-risk settlement of large value funds transfers between financial institutions. It also facilitates the settlement of fixed income security trades, FX trades, and other financial market transactions. By settling retail payment clearing results, the
PhilPaSSplus ensures that individuals, businesses and the government can securely send and receive money through several channels – check, ATM, InstaPay and PESONet. It operates daily from 9:00AM to 5:45PM, Mondays through Fridays.
1Definition is mainly drawn from the document
A glossary of terms used in the payments and settlement systems (2016) published by the Committee on Payments and Market Infrastructures (CPMI).
A Brief History of the
PhilPaSSplus
In October 1995, the Multi-transaction Interbank Payments System (MIPS) was adopted by the Bangko Sentral ng Pilipinas (BSP), allowing payment instructions to be directly debited against the demand deposit accounts banks maintained with the BSP. While the system incorporated batched settlement, it was still manual intensive and report generation was limited.
The payment system was then upgraded in 2002 to the highly automated
Philippine Payment and Settlement System or
PhilPaSS, which allowed real-time or near real-time settlements and more system generated reports.
PhilPaSSplus was adopted in 2021. It features greater settlement capacity and efficiency, stronger security features, broader access channels, better interoperability and payment information.
RTGS System Features
-
Payment Queuing & Reprioritization - Instructions that cannot be settled due to insufficient funds are held on queue until funds are made available
-
Payment Warehousing - Participants can warehouse transactions up to four (4) calendar days.
-
Gridlock resolution - The system initiates a gridlock resolution whenever two (2) or more instructions remain unsettled
-
Transaction Validation - Payment instructions are subject to validation
-
Reporting - Participants may generate various reports, such as account balance report, statement of account, transactions summary, and others
-
Audit Trail - The system maintains audit records
-
Payment Status Validation - Participants can verify the settlement status of their transactions
-
System Inquiries - Participants can send inquiries and/or requests through the system
PhilPaSSplus includes two new features:
-
ISO 20022-Compliant - The system and its participants are compliant with the ISO 20022 international messaging standard, which facilitates interoperability with domestic and international payment systems.
-
Intraday Settlement Facility (ISF) - This facility may be used by participants needing additional liquidity during daily operations. Availments must be settled by the end of the day the ISF was availed to avoid incurring charges. For more information on the ISF, please refer to the ISF FAQs.
Transactions settled through the
PhilPaSSplus
- Movements of funds between the individual participants' proprietary accounts
- Interbank/inter-institution transfers for proprietary transactions
- Interbank/inter-institution transfers for further credit to customer accounts
- Government collections and disbursements
- Withdrawals from and deposits into the accounts maintained with the BSP
- The money settlement leg of security trades
- The Peso leg of FX trades
- Settlements related to the BSP’s ISF
- Transactions with the BSP Financial Markets, including placements in deposit facilities and maturities of deposits, availments and maturities of the Overnight Lending Facility, and purchase or sale of FX and securities
- Clearing results for checks, automated teller machine (ATM) transactions, digital payments, and other types of retail payments
- Other large value transactions or those that are not considered as retail payments under BSP regulations
The Peso RTGS Payment System
PhilPaSSplus participants are comprised of the following:
-
Participants with Settlement Accounts: These include banks, non-bank financial institutions with quasi-banking functions, non-bank electronic money issuers, and government agencies, as well as Bangko Sentral units that conduct monetary operations and those responsible for disbursing and receiving funds on behalf of the Bangko Sentral.
-
Sponsored Participants: These are financial institutions sponsored into settlement by participants with settlement accounts through the RTGS system.
-
Financial Market Infrastructures (FMIs): These are infrastructures that are interlinked with the RTGS system to enable settlement of security, foreign exchange (FX), and other financial market transactions in accordance with the DvP and PvP mechanisms, which minimize the principal risk associated with such transactions.
-
Clearing Switch Operators (CSOs): These are clearing organizations that are permitted to interconnect with the RTGS system for purposes of settling retail payments in accordance with the National Retail Payment System regulatory framework.
-
Critical Service Providers (CSPs): These are technology companies that provide solutions which are vital to the operation of the RTGS.
Participant financial institutions, CSOs, FMIs, and CSPs join the Peso RTGS system or
PhilPaSSplus in forming part of the RTGS payment system.
Governance and Supervision
The BSP, through its
Peso RTGS Management Committee, operates the Peso RTGS system. This Committee is composed of a Chairperson and the heads of the BSP units that are involved in sustaining the sound and smooth functioning of this payment system.
In addition, the Peso RTGS PS has been designated as a
Systemically Important Payment System (SIPS) by the BSP Monetary Board given its critical role in the efficient and secure movement of funds in the financial system and the economy in general. As a SIPS, the Peso RTGS PS is subject to closer supervision by the BSP for the protection of the participating institutions and financial consumers.
Messaging Channels
Payment instructions are made through three messaging channels:
- Participant Browser, a web-based messaging system provided by the BSP to certain RTGS PS participants
- SWIFT, an internationally accepted messaging system that runs through a leased line
- Virtual Private Network (VPN) – Straight Through Processing (STP) - A communication module that provides a means of message exchanges between the RTGS system and the participants’ platforms via VPN
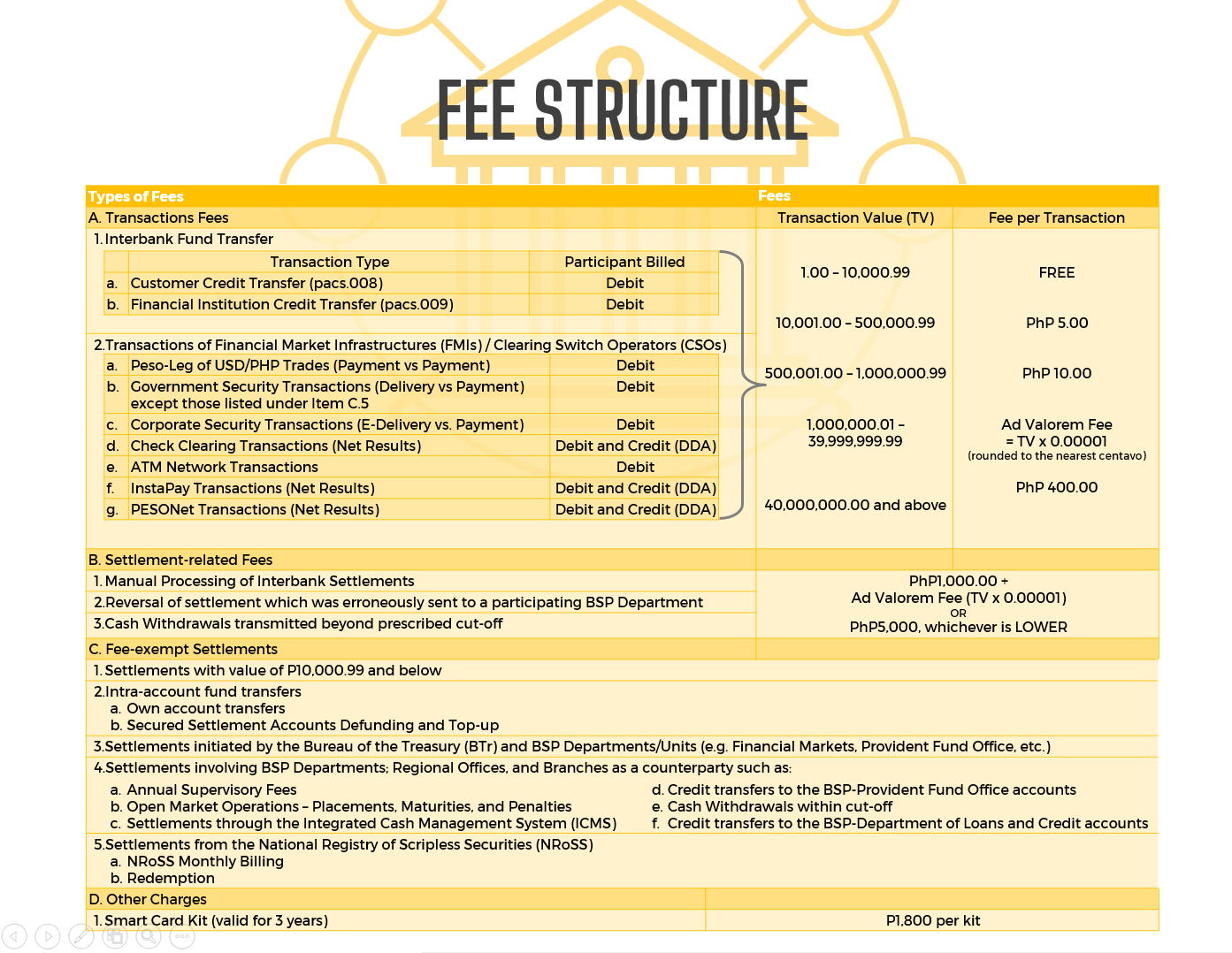
Fee Structure
What is
PhilPaSSplus?
Download
